Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuo, Yoji*; Shinohara, Satoshi*; Mori, Shigeo*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.966 (Internet), 6 Pages, 2007/03
Change of the charge ordered (CO) structure by substituting Cu for Fe
for Fe in LuFe
in LuFe O
O was investigated by means of the transmission electron microscopy. The CO structure in LuFe
was investigated by means of the transmission electron microscopy. The CO structure in LuFe O
O is characterized by the modulated structure with the wave vector of q=1/3[1 -1 3/2] and the average size of the CO domains can be estimated to be about 10-20nm. On the contrary, the Cu
is characterized by the modulated structure with the wave vector of q=1/3[1 -1 3/2] and the average size of the CO domains can be estimated to be about 10-20nm. On the contrary, the Cu substitution destroyed the CO structure drastically and induced characteristic local lattice distortion, which gives rise to characteristic diffuse scattering in the reciprocal space. High-resolution lattice images revealed that there exist nano-scale clusters, which are characterized as the short-range ordering of the Cu
substitution destroyed the CO structure drastically and induced characteristic local lattice distortion, which gives rise to characteristic diffuse scattering in the reciprocal space. High-resolution lattice images revealed that there exist nano-scale clusters, which are characterized as the short-range ordering of the Cu and Fe
and Fe ions on the triangular lattice. In addition, the magnetic measurement revealed that LuFeCuO
ions on the triangular lattice. In addition, the magnetic measurement revealed that LuFeCuO exhibits an antiferromagnetic transition around 50K, which is lower than the Neel temperature of 250K in LuFe
exhibits an antiferromagnetic transition around 50K, which is lower than the Neel temperature of 250K in LuFe O
O .
.
Ikeda, Naoshi*; Mori, Shigeo*; Yoshii, Kenji; Matsuo, Yoji*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.966 (Internet), 9 Pages, 2007/03
We report ferroelectricity in the triangular mixed valence material RFe O
O (R=Y, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). This ferroelectricity originates from the polar ordering of Fe
(R=Y, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). This ferroelectricity originates from the polar ordering of Fe and Fe
and Fe or the polar ordering of electrons on Fe
or the polar ordering of electrons on Fe . The electric polarization arising from such electron ordering may not couple with the lattice modulation. The ordering process of Fe
. The electric polarization arising from such electron ordering may not couple with the lattice modulation. The ordering process of Fe and Fe
and Fe is explained by the frustrated interaction of charges in a triangular lattice. The ferroelectric property of this material is present at room temperature.
is explained by the frustrated interaction of charges in a triangular lattice. The ferroelectric property of this material is present at room temperature.
Oi, Takao; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Inagaki, Manabu; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Sone, Tomoyuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Ebashi, Takeshi; Nakajima, Kunihiko*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.985, p.129 - 134, 2007/00
A comprehensive sensitivity analysis method has been developed with the aim of providing quantitative information in an efficient manner. This methodology is composed of the following two components: (1) a statistical method with random sampling of independent parameters, which identifies important parameters and extracts threshold values of parameters and/or combinations yielding a "successful condition" where maximum dose does not exceed a target value, (2) A nuclide migration model that as far as possible incorporates a comprehensive set of phenomena occurring within the repository. This approach was applied as part of a safety assessment of the geological disposal of TRU waste in Japan (TRU-2). It was shown that the concept of TRU waste disposal is robust from the point of view of safety.
 and NpTGa
and NpTGa
Metoki, Naoto
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.986, p.89 - 100, 2007/00
The results of our recent neutron scattering studies on actinide 115 compounds are reviewed. The itinerant many body f electron system and cross over to the localized character are realized only in actinide system. Actinide 115 family is very interesting, because we can grow high quality single crystals of many iso-structural compounds with different number and character of f electrons and valence d electrons. Variety of the ground state have been reported, e.g. paramagnetic, itinerant magnetism, and heavy fermion superconductivity in PuCoGa . Very recently we have intensively studied the magnetic structure in UTGa
. Very recently we have intensively studied the magnetic structure in UTGa and NpTGa
and NpTGa , These compounds exhibit a variety of the magnetic structure with A-, C-, G-type antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic ordering and canted structure. NpFeGa
, These compounds exhibit a variety of the magnetic structure with A-, C-, G-type antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic ordering and canted structure. NpFeGa exhibits an unusual magnetic anisotropy with the direction of the magnetic moment inclined about 25 degrees from the tetragonal basal plane. On the other hand, the localized compounds RRhIn
exhibits an unusual magnetic anisotropy with the direction of the magnetic moment inclined about 25 degrees from the tetragonal basal plane. On the other hand, the localized compounds RRhIn (R: Tb, Ho, Dy, Nd) shows the antiferromagnetic structure with
(R: Tb, Ho, Dy, Nd) shows the antiferromagnetic structure with  =(1/2 0 1/2). The magnetic moment is parallel to the c-axis. An identical magnetic structure in rare earth compounds is a consequence of the localized nature of 4
=(1/2 0 1/2). The magnetic moment is parallel to the c-axis. An identical magnetic structure in rare earth compounds is a consequence of the localized nature of 4 electrons. We found that NpFeGa
electrons. We found that NpFeGa , NpNiGa
, NpNiGa , and NpRhGa
, and NpRhGa exhibit 5
exhibit 5 electronic transition between the low- and high-moment states associated with a change in the direction of the magnetic moment. The diverse magnetic ordering and the 5
electronic transition between the low- and high-moment states associated with a change in the direction of the magnetic moment. The diverse magnetic ordering and the 5 electronic transition suggest that the orbital degree-of-freedom of itinerant 5f electrons may play important role for the physical properties in many body
electronic transition suggest that the orbital degree-of-freedom of itinerant 5f electrons may play important role for the physical properties in many body  electron systems. Actually a localized model predicts the magnetic structure and the phase diagram with magnetic and quarupolar order parameters. A resonant X-ray scattering study is in progress, if the predicted antiferroquadrupole order coexists with the canting antiferromagnetic dipole order in NpNiGa
electron systems. Actually a localized model predicts the magnetic structure and the phase diagram with magnetic and quarupolar order parameters. A resonant X-ray scattering study is in progress, if the predicted antiferroquadrupole order coexists with the canting antiferromagnetic dipole order in NpNiGa .
.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Saito, Hiroyuki; Utsumi, Wataru
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.987, p.73 - 78, 2007/00
In-situ X-ray diffraction study revealed that there were two distinct structures of fluid phosphorus and a sharp transition occurred between them at about 1 GPa. The two structures, one is molecular fluid and the other is polymeric fluid, have different densities. By an X-ray radiography method, macroscopic separation of two fluid phases was directly observed. These results support a view that it is a first-order phase transition. To study solidification of low-density, high-density fluids and their mixture, an X-ray radiograph has been recorded during a rapid cooling using a cubic-type multi-anvil apparatus installed on a beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8. The obtained solid sample was investigated by an optical microscope and by an electron microscope. The low-density fluid tends to transform to a kind of red phosphorus while high-density fluid usually transforms to black phosphorus. Several shapes of grains were obtained from mixture.

Haga, Yoshinori; Aoki, Dai*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Yamagami, Hiroshi*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Shiokawa, Yoshinobu; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Arai, Yasuo; Onuki, Yoshichika*
no journal, ,
Plutonium compounds is located at the boundary between itinerant 5f states in the light actinides and the localized 5f states in the heavier actinides. To understand the electronic states, experimental observation of the Fermi surfaces is quite important. Actually we have already shown in a variety of uranium compounds that the 5f electrons in uranium compounds is, in most cases, itinerant. For plutonium compounds, however, experiments are extremely difficult because of its radioactivity. Recently, we have demonstrated that the 5f electrons of a plutonium compound PuIn forms Fermi surfaces with itinerant 5f electrons.
forms Fermi surfaces with itinerant 5f electrons.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo; Matsuzawa, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
First-principles method is applied to assess the embrittlement mechanism of bcc iron (Fe) grain boundaries due to the segregation of various solutes (C, Si, P, S, Mn, Cr, Cu, Mo, etc.) that are contained, for example, in the nuclear reactor pressure vessel steel. The simulation is performed for the bcc Fe  3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary to evaluate the effects of solute segregation on the strength of the interface separation, in particular, focusing on the mechanism and degree of embrittlement. We discuss the relative effects of these solutes on the embrittlement mechanism and segregation energy.
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary to evaluate the effects of solute segregation on the strength of the interface separation, in particular, focusing on the mechanism and degree of embrittlement. We discuss the relative effects of these solutes on the embrittlement mechanism and segregation energy.
Li, J.*; Shimizu, Futoshi; Ogata, Shigenobu*
no journal, ,
Shear bands form in most bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) within a narrow range of uniaxial strain 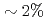 . We propose this critical condition corresponds to embryonic shear band (ESB) propagation, not its nucleation. To propagate an embryonic shear band, the far-field shear stress must exceed the quasi steady-state glue traction of shear-alienated glass until the glass-transition temperature is approached due to frictional heating, at which point ESB matures as a runaway shear crack. The incubation lengthscale necessary for this maturation is predicted to be
. We propose this critical condition corresponds to embryonic shear band (ESB) propagation, not its nucleation. To propagate an embryonic shear band, the far-field shear stress must exceed the quasi steady-state glue traction of shear-alienated glass until the glass-transition temperature is approached due to frictional heating, at which point ESB matures as a runaway shear crack. The incubation lengthscale necessary for this maturation is predicted to be 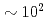 nm for Zr-based BMGs, below which sample-scale shear localization does not happen. Molecular dynamics simulations with up to 20-million atoms have directly verified the aged-rejuvenation-glue-liquid (ARGL) shear band structural model and "march-to-melting" instability, which occurs with a characteristic incubation timescale of
nm for Zr-based BMGs, below which sample-scale shear localization does not happen. Molecular dynamics simulations with up to 20-million atoms have directly verified the aged-rejuvenation-glue-liquid (ARGL) shear band structural model and "march-to-melting" instability, which occurs with a characteristic incubation timescale of 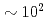 ps and lengthscale of
ps and lengthscale of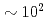 nm.
nm.